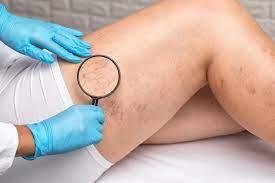
If you’re like most people, you probably don’t think too much about your veins. But if you’re experiencing any type of pain or discomfort in your extremities, you should definitely consult a vein clinic. Vein clinics are a fantastic resource for those who want to learn more about their veins and the various diseases that can affect them. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the most common Vein Disease and what you can do to prevent them. From understanding your cholesterol levels to recognizing warning signs for stroke, read on to learn everything you need to know about vein health and how to keep yourself safe.
What Vein Diseases are There?
Vein diseases are a common problem for many people. They can cause pain, redness, and swelling in your veins. If you have any of these symptoms, you should go see a doctor. Vein diseases can be caused by many things, including genetics, lifestyle factors, and health conditions.
Some vein diseases are more common than others. The most common vein disease is high blood pressure. Other common vein diseases include:
-Athlete's foot: This is an infection of the skin on the bottom of your feet. It causes intense itching and may lead to fungal overgrowth (which can cause permanent damage to the nail bed), inflammation, and scarring. Athletes' foot is most often caused by a fungus called Trichophyton rubrum. You can get athlete's foot from close contact with someone who has it or by walking or swimming in wet areas where the fungus grows easily (such as in locker rooms).
-Varicose veins: Varicose veins are swollen veins near your ankles or thighs. They can become enlarged due to long-term hypertension (high blood pressure) or other lifestyle factors, such as being overweight or having high cholesterol levels. Varicose veins may also develop if you have diabetes mellitus or if you have had a previous surgery that removed part of your leg (such as multiple knee surgeries).
The Types of Vein Diseases
vein disease is a widespread problem that affects the entire body. Depending on the type of vein disease, symptoms can vary, but most tend to cause pain and fatigue. Vein diseases are typically caused by problems with the veins themselves, such as blockages or varicosities. Treatment generally involves using various methods to clear the blockage or improve vein function.
The Causes of Vein Diseases
The most common type of vein disease is varicose veins. These are small, dilated veins that can become swollen and twisted. Vein diseases can also cause pain and difficulty walking. Many other types of vein problems also occur, such as spider veins (small raised bumps on the skin due to varicose veins), thrombosis (a blood clot in a vein), and lupus erythematosus (a condition that causes red patches on the skin and tissues).
How to Diagnose Vein Disease
Vein disease is a term used to describe any condition that affects the veins in your body. There are many different types of vein disease, and each can cause different symptoms. If you experience any unusual pain or swelling in your leg, arm, or hand, it's important to see a doctor for an evaluation. Here are some tips on how to diagnose vein disease:
1. Inspect the skin around the affected area for any signs of inflammation or redness.
- Check for calf tenderness when standing or walking; this may indicate a venous insufficiency (a deficiency in blood flow to the legs).
- Take a blood pressure reading; high readings may indicate atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) or other forms of heart disease, which can lead to venous obstruction.
- Do an ultrasound exam if there is suspicion of an issue with the veins near your heart. This exam uses sound waves and images to view small structures inside the body; it can identify problems with veins and other organs near your heart.
Treatment Options for Vein Diseases
There are a number of ways to treat vein diseases, and your doctor will decide what is best for you. Treatment options include medications, surgeries, and other treatments.
Medications
Some common vein medications include:
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) lower blood pressure and help prevent heart attacks by reducing the amount of fluid retention in the body. They also reduce the risk of clots forming in the veins. ACE inhibitors are used to treat many types of blood pressure problems, including hypertension (high blood pressure), but they can also be used to treat benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH).
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) work similarly to ACE inhibitors but they don't have as many side effects. ARBs are used primarily to treat hypertension, although they can be prescribed for other conditions as well.
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) decrease the amount of blood that flows through narrowed veins by blocking calcium from entering the cells. CCBs are often prescribed to treat high blood pressure and can also be used for other conditions such as atrial fibrillation (a type of irregular heart rhythm).
- Beta blockers block the adrenaline rush that leads to an increase in heart rate. These medications are commonly used to prevent cardiac arrest or stroke, but they may also be prescribed for other conditions such as anxiety or chronic pain.
Conclusion
Vein disease is a major global health concern, affecting more than 50 million people worldwide. As such, it's important to know what Vein Clinic can teach you about vein diseases and how to prevent them. By visiting our clinic and receiving the appropriate treatment, you can help prevent these conditions from damaging your veins and lead to even greater complications down the road. Thanks for reading!