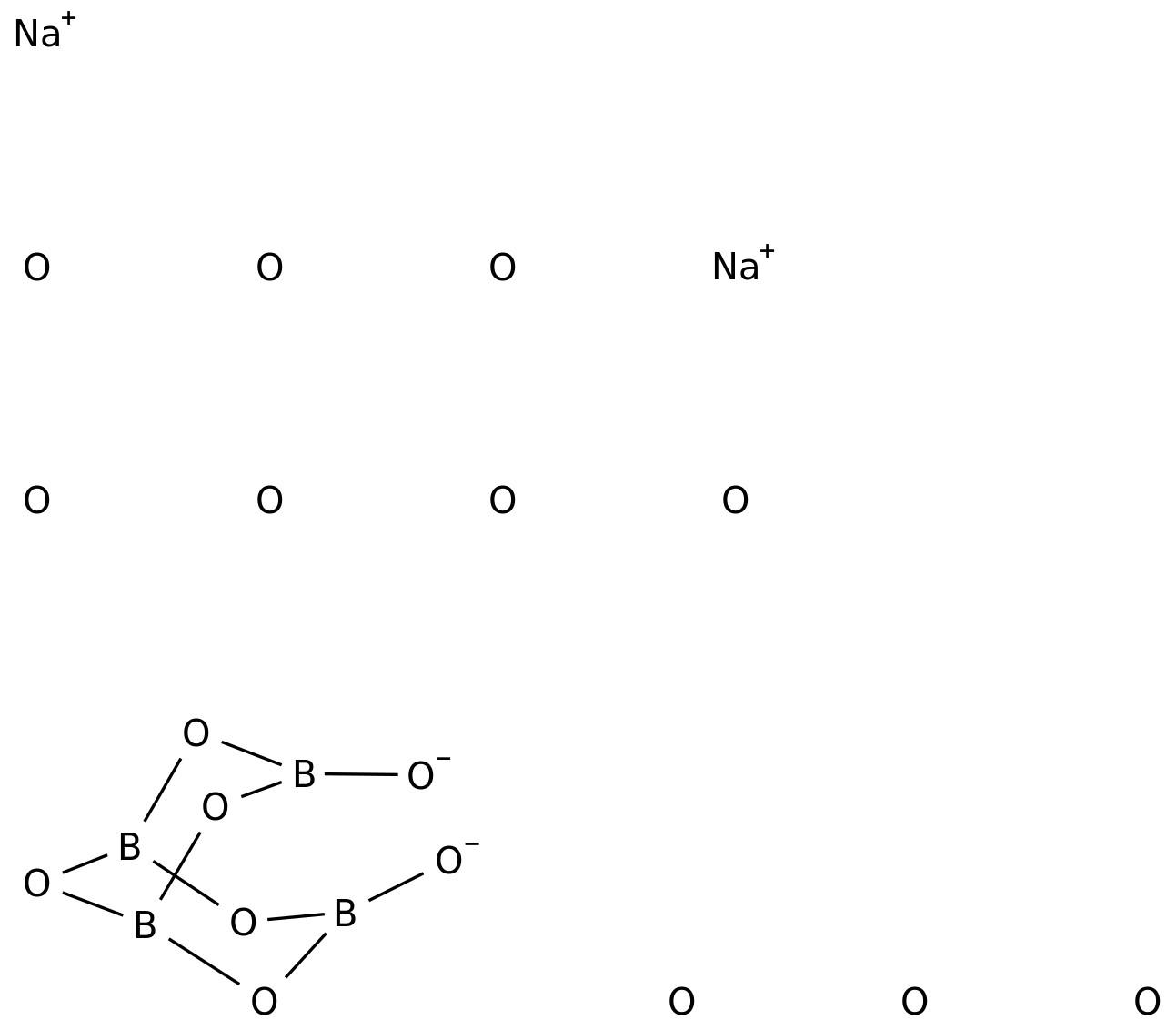
Borax is a natural mineral with a chemical formula Na2B4O7 • 10H2O. Borax also is known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate. It is one of the most important boron compounds. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name for what is borax sodium tetraborate decahydrate.
Borax Versus Boric Acid
Borax and boric acid are two related boron compounds. The natural mineral, mined from the ground or collected from evaporated deposits, is called what is borax. When borax is processed, the purified chemical that results is boric acid (H3BO3). Borax is a salt of boric acid. While there are some differences between the compounds, either version of the chemical will work for pest control or slime.
How Safe Is Borax?
Borax in the usual form of sodium tetraborate decahydrate is not acutely toxic, which means a large amount would need to be inhaled or ingested to produce health effects. As far as pesticides go, it's one of the safest chemicals available. A 2006 evaluation of the chemical by the U.S. EPA found no signs of toxicity from exposure and no evidence of cytotoxicity in humans. Unlike many salts, skin exposure to what is borax does not produce skin irritation.
However, this doesn't make borax categorically safe. The most common problem with exposure is that inhaling the dust can cause respiratory irritation, particularly in children. Ingesting large amounts of borax can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The European Union (EU), Canada, and Indonesia consider borax and boric acid exposure a potential health risk, primarily because people are exposed to it from many sources in their diet and from the environment. The concern is that overexposure to a chemical generally deemed safe could increase the risk of cancer and damage fertility. While the findings are somewhat contradictory, it's advisable children and pregnant women limit their exposure to borax if possible.